Solar energy has become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners and businesses alike looking to reduce their energy bills and their carbon footprint. But, like any investment, adopting solar energy as a long-term solution requires careful consideration. The question many people ask themselves is: Is solar a good long term investment? With the promise of energy independence, tax incentives, and potential savings, it’s tempting to dive in, but it’s important to understand the full picture.
What Does It Mean to Invest in Solar Energy?
Before diving into whether solar energy is a good long-term investment, it’s important to first understand what it means to invest in solar. At its core, investing in solar means paying for a solar energy system upfront with the expectation that you’ll save money on energy bills in the future. However, like all investments, it comes with both costs and rewards that play out over time.
Understanding Solar Investments
When you decide to invest in solar energy, you’re purchasing and installing a solar panel system on your property (or entering a solar lease agreement). This system harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity to power your home or business.
The most common types of solar investments are:
- Residential Solar Panels: Homeowners purchase solar panels for their homes, either fully or with the help of financing options like loans or leases.
- Commercial Solar Systems: Businesses also invest in solar energy to reduce operating costs and demonstrate sustainability.
- Solar Stocks and Funds: For those not ready to install solar panels themselves, investing in solar companies through stocks or mutual funds is another way to get involved in the solar energy market.
Each type of solar investment comes with its own set of financial considerations and benefits, which we will explore in more detail later.
How Solar Works as an Investment
Solar systems typically have a lifespan of 25-30 years, meaning the financial benefits are long-term. Over time, the savings generated from reduced utility bills (due to less reliance on the grid) generally offset the initial cost of installation. However, to fully reap the benefits, it’s important to think beyond the upfront costs. The key here is return on investment (ROI). For solar to be a sound financial decision, the long-term savings need to be greater than the cost of installation and maintenance.
The ROI for solar panels can vary depending on your location, the size of your system, and the financing method you choose. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, most homeowners will see a return on their solar investment within 6-10 years, with the systems lasting 20-30 years beyond that.
How Solar Can Be a Long-Term Investment
1. Solar Energy’s Cost Saving Potential
One of the most compelling reasons to invest in solar energy is the potential for long-term cost savings. Installing solar panels allows you to generate your own electricity, which means you no longer have to rely entirely on your utility company. This can lead to significant reductions in your energy bills.
How Much Can You Save?
While the savings from solar energy will vary based on several factors, here are some general estimates:
- Average Savings for Homeowners: A typical residential solar system can save homeowners $10,000 to $30,000 over 20 years. In some cases, savings can be even greater depending on location, energy consumption, and utility rates.
- Annual Savings: Homeowners can expect to save anywhere from $500 to $2,000 per year on average.
By producing your own electricity, you’re no longer subject to fluctuating utility prices. This is especially valuable in areas where utility rates are rising year after year. For example, in states like California and New York, solar can be particularly cost-effective because utility rates are higher than in other parts of the country.
Decreased Energy Costs Over Time
It’s important to note that energy prices tend to rise over time. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), electricity prices have increased by around 2-3% per year on average. By investing in solar, you’re essentially locking in a stable energy cost for the long term, protecting yourself against future price hikes.
The combination of lower monthly energy bills and protection from future price increases makes solar a solid long-term investment.
Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI for solar energy is generally positive, especially when considering that solar systems last for decades. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the average residential solar system will pay for itself in around 6 to 10 years. After that, the system continues to produce energy with little to no cost (aside from maintenance and minor repairs). The savings you accrue after the payback period are essentially profit.
| Factor | Average ROI |
|---|---|
| System Cost | $10,000 – $30,000+ |
| Payback Period | 6-10 years |
| Annual Savings | $500 – $2,000+ |
| Total Savings Over 25 Years | $15,000 – $60,000+ |
2. Solar Panel Lifespan and Durability
When considering the longevity of your investment, it’s essential to know how long solar panels will last and what to expect in terms of performance over time.
How Long Do Solar Panels Last?
The typical lifespan of solar panels is 20-30 years. While they may begin to lose efficiency slightly after the first 10 years, the rate of decline is relatively slow. On average, solar panels lose about 0.5% to 1% of their efficiency per year. By the time your system reaches 25 years of use, it may still be operating at 80% or more of its original capacity.
Warranty and Maintenance
Most solar panels come with 25-year warranties, which cover performance and defects. This means that if your panels underperform or break prematurely, they can be replaced or repaired at no extra cost.
In terms of maintenance, solar panels require very little upkeep. An annual cleaning and inspection by a professional solar technician is often enough to ensure your system continues to operate efficiently. This low maintenance requirement further enhances the long-term value of solar as an investment.
Performance Over Time
The performance of solar panels over time can be influenced by several factors, including climate, shading, and panel quality. However, most systems will continue to generate power for 20-30 years, providing significant savings and energy generation even as they age.
Pros of Solar as a Long Term Investment
While the potential for significant savings and a stable energy supply are major selling points, there are other compelling advantages to investing in solar energy that go beyond just the financials.
1. Significant Long-Term Savings
As mentioned earlier, one of the biggest draws of solar energy is its potential for long-term savings. Beyond reducing monthly energy bills, solar can bring financial benefits that accumulate over time.
How Much Can You Save in 10, 20, or 30 Years?
The long-term savings from solar energy can be staggering, especially in regions with high utility rates or strong sunlight. Here’s a breakdown of how much you could save:
- 10 years: In the first decade, you may save anywhere between $5,000 and $20,000, depending on the size of your system, energy usage, and location.
- 20 years: Over a 20-year period, savings could range from $15,000 to $40,000, as the system reaches its payback period and continues to operate at a high efficiency.
- 30 years: By the 30-year mark, you could have saved anywhere from $30,000 to $70,000 or more, depending on your area and energy habits.
These savings represent money that would otherwise go to your energy provider. Solar panels essentially turn that money into equity in your property or into direct savings for your business.
How Solar Saves You Money in the Long Run
- Eliminate or Reduce Energy Bills: In many cases, solar can completely eliminate your energy bills, depending on the size of your system and your energy consumption. This is especially true for homeowners with high energy demands or businesses that operate around the clock.
- Tax Incentives and Rebates: As previously mentioned, solar installations often come with significant tax incentives and rebates, which help reduce the initial investment cost. This makes it easier to see a return on investment (ROI) sooner.
- Increased Efficiency Over Time: With new advancements in solar technology and more efficient panels, homeowners and businesses can enjoy greater energy savings year after year.
2. Increasing Property Value
Another significant benefit of solar panels is their ability to increase property value. A number of studies have shown that homes with solar systems tend to sell for more than comparable homes without them.
How Solar Panels Increase Home Value
Homes with solar systems are generally perceived as more attractive due to their lower energy costs, and this can make them more valuable in the real estate market. According to a 2019 study by the U.S. Department of Energy, homes with solar panels sold for an average of 4.1% more than homes without solar.
For example, if your home is worth $300,000, a solar system could increase its value by $12,300. This increase in value is not just based on energy savings; it also reflects a growing consumer interest in energy-efficient homes and sustainability.
Are Solar Homes Selling Faster?
In addition to increasing home value, homes with solar panels may sell faster than homes without. Solar energy is becoming a sought-after feature among homebuyers, especially those looking to reduce their energy costs. Homebuyers are increasingly drawn to homes that already have solar systems installed because it means they don’t have to deal with the hassle or upfront cost of installation themselves.
A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that homes with solar panels sell 20% faster than those without, which is another reason why solar can be a great long-term investment.
3. Energy Independence and Stability
Investing in solar energy offers more than just financial savings – it also gives you a sense of energy independence. With solar panels, you’re less reliant on the grid, which can be a crucial factor as electricity rates rise or during times of energy shortages.
The Role of Solar in Energy Security
Solar panels can help homeowners and businesses maintain a level of energy security. When you’re producing your own electricity, you’re less vulnerable to power outages or disruptions in the grid. In some areas, especially where power outages are frequent, solar with battery storage offers the added benefit of having electricity even when the grid goes down.
Hedge Against Rising Energy Prices
One of the most significant risks of not investing in solar is the continued rise in energy prices. Over the past few decades, utility rates have consistently increased, and this trend is likely to continue. Solar provides a built-in hedge against these price hikes, allowing you to control your energy costs for the long term.
By locking in energy costs through a solar system, you’re not only protecting yourself from price volatility but also potentially insulating yourself from future price hikes caused by inflation, supply chain issues, or political instability.
4. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Beyond the financial benefits, solar energy is an environmentally friendly investment. As more people and businesses seek sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, solar energy stands out as one of the cleanest options available.
Contributing to Renewable Energy Goals
Solar power is a renewable resource, which means it doesn’t deplete natural resources or contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. By investing in solar, you’re helping reduce your carbon footprint and contributing to a cleaner, greener world.
For those with long-term environmental goals, solar can be a way to make a tangible impact. Governments and organizations around the world are pushing for greater adoption of renewable energy sources to meet climate targets. By choosing solar, you’re aligning your investment with these global sustainability efforts.
Eco-Friendly and Green Investment
Solar energy doesn’t just reduce your energy bills—it also reduces your reliance on fossil fuels, which are responsible for a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy solutions, investing in solar is a way to be part of this change.
Potential Risks and Challenges of Solar as a Long Term Investment
While the benefits of investing in solar energy are clear, it’s important to acknowledge that there are some risks and challenges associated with this investment. No financial decision is without its drawbacks, and it’s essential to fully understand both the pros and cons of solar energy before making the leap.
1. High Initial Costs
One of the main obstacles to adopting solar energy is the upfront cost of installation. While the cost of solar panels has decreased over the years, the initial investment can still be substantial, especially for residential installations. Depending on the size of your system and your location, the average cost for a solar panel installation ranges between $10,000 and $30,000 (before tax credits).
Financing Options for Solar
Fortunately, there are several financing options that can make solar more accessible:
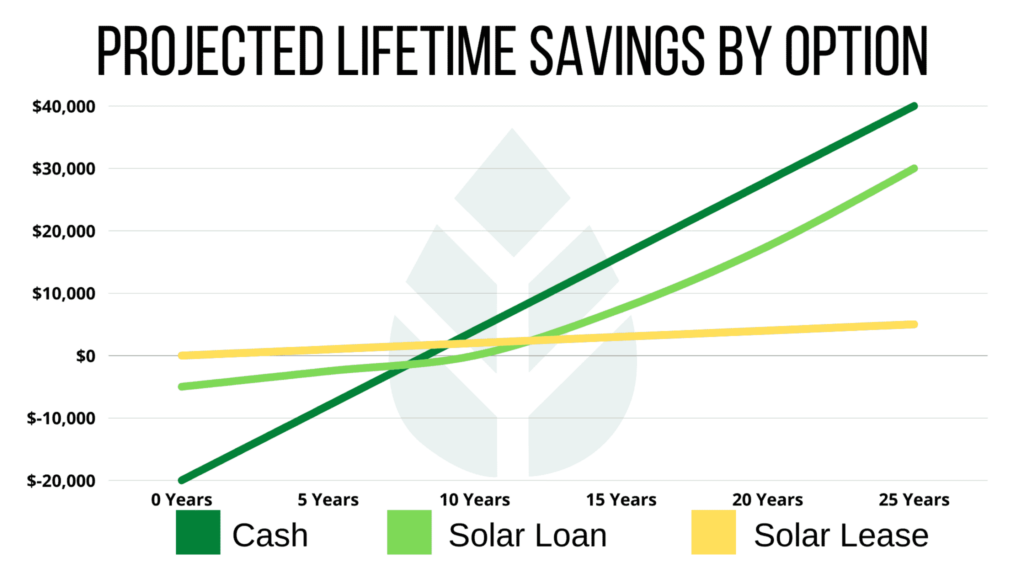
- Solar Loans: You can take out a loan to cover the cost of installation, and then pay it back over time. With this option, you’ll own the system outright once the loan is paid off.
- Leases and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): These options allow you to install solar panels with little to no upfront cost, though you’ll have to pay a monthly lease or energy cost to the solar provider.
Despite these financing options, the upfront cost remains a significant hurdle for some, making it important to evaluate your financial situation carefully before committing.

Potential Risks and Challenges of Solar as a Long Term Investment
While solar energy presents many exciting advantages, it’s important to understand that, like any investment, it does come with certain risks and challenges. These factors could affect your decision to install solar panels and the overall return on investment (ROI) you can expect over the long term.
1. High Initial Costs
As discussed earlier, the initial investment required to install a solar system can be a barrier for many. While prices have come down significantly in the past decade, the cost of installing a solar panel system still averages between $10,000 and $30,000 for residential setups.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Solar Installation
Several factors can influence the upfront costs of a solar installation:
- System Size: Larger systems with more panels and higher energy production capacities will naturally cost more.
- Roof Type and Size: The complexity of your roof and the space available for panels can impact installation costs. Roofs that require extra reinforcement or have unusual angles can make the installation process more expensive.
- Location: The cost of solar installation varies by region. Areas with higher labor costs or stricter regulations may face higher installation fees.
- Energy Needs: Homes or businesses with higher energy consumption will need larger systems, which will be more expensive.
Financing Solar Panels
While the upfront costs can be steep, various financing options help ease the financial burden:
- Solar Loans: With a solar loan, you can spread out the payments over several years, typically 5-20 years. Many homeowners will save enough on energy bills during this time to offset loan payments.
- Leases and PPAs: These options allow you to install solar with little to no upfront costs, but they do come with monthly payments or long-term contracts. The downside is that you won’t own the system, and savings may be less than if you were to purchase the system outright.
While financing options make solar more accessible, the need to finance the system does mean you’ll be paying interest or ongoing costs over time. For some, this can diminish the investment’s overall appeal, particularly if the savings from the solar system don’t fully offset the cost of financing.
2. Energy Production Variability
Another consideration when thinking about solar as a long-term investment is the variability in energy production. Solar panels rely on sunlight to generate electricity, meaning their energy output is subject to weather conditions, seasons, and geographical location.
Weather and Location Factors
Solar energy production can vary depending on several factors:
- Sunlight Hours: Regions with more sunlight (e.g., Arizona, California) will see higher energy production from solar panels. In contrast, areas with frequent cloud cover or shorter days during the winter (e.g., the Pacific Northwest or northern Europe) will produce less energy.
- Seasonal Variations: Solar energy production is highest in the summer months when days are longer, and the sun is more intense. During the winter months, energy output can be significantly lower, which may impact the savings you expect from solar.
- Geographical Location: Some locations simply have more hours of sunlight per day on average, which means a solar system will produce more energy in those regions compared to others.
For example, a solar system in Seattle (which gets an average of 140 sunny days per year) may produce much less electricity than a system in Phoenix (with 300+ sunny days per year).
Managing Energy Production Variability
One way to mitigate the impact of weather-related energy fluctuations is by installing a solar battery system. Solar batteries, like the Tesla Powerwall or LG Chem, store excess energy produced during sunny days so that it can be used when sunlight is not available, such as at night or during cloudy days. While batteries can add to the overall cost, they can provide additional energy security, particularly in regions with unreliable grids or frequent power outages.
3. Changing Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives have played a critical role in making solar energy more affordable. However, these incentives can change over time, which may impact the financial viability of solar as a long-term investment.
The Future of Solar Tax Incentives
One of the key financial incentives for solar energy is the federal solar tax credit, also known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This tax credit allows homeowners and businesses to deduct up to 30% of the cost of a solar system from their federal taxes. However, this tax credit is set to decrease in the coming years.
For example:
- In 2023, the ITC was 30% for both residential and commercial installations.
- In 2024, it’s expected to decrease to 26% for residential systems and continue declining in future years.
This means that if you’re considering solar, it may be wise to act sooner rather than later to maximize your tax savings.
Risk of Incentive Cuts
While the federal tax credit is a significant benefit, there’s always a risk that government incentives could be cut or changed in the future. For example, some states may phase out or reduce local rebates or net metering policies (which compensate solar owners for excess energy sent back to the grid). This could impact the financial attractiveness of solar for some potential investors.
Although solar is still a good investment in many areas, the reliance on government incentives means that future policy changes could potentially affect the investment’s profitability.
Solar vs. Other Long-Term Investment Options
As we’ve explored, solar energy can offer significant financial benefits in the long run. However, before deciding whether it’s the right investment for you, it’s helpful to compare solar to other popular long-term investment options.
1. Comparing Solar to Stock Market Investments
Many people consider traditional investments like stocks or bonds when thinking about long-term financial growth. So, how does solar compare?
Risk-Return Profile
- Stocks and Bonds: The stock market is known for its potential for high returns, but it comes with considerable risk. Stock prices can fluctuate wildly, and there’s no guarantee that an investment will yield a positive return. Bonds tend to be more stable but offer lower returns.
- Solar Energy: Solar provides a more stable and predictable return. While the returns aren’t as high as some stocks, solar offers consistent savings that are relatively unaffected by market volatility. Over the long term, solar can provide a guaranteed return, especially with utility prices expected to rise.
Volatility vs. Stability
While the stock market can provide high returns, it’s also much riskier. Solar, by contrast, offers a more stable investment. It’s not subject to the same level of market fluctuations, which can make it a more attractive option for risk-averse investors.
2. Solar vs. Real Estate as an Investment
Real estate is often viewed as a reliable long-term investment, and for good reason. Real estate properties tend to appreciate over time. But how does solar compare?
Appreciation Potential
- Real Estate: Historically, real estate appreciates over time, although the rate of appreciation can vary depending on location, market conditions, and other factors. Real estate also offers the possibility of rental income.
- Solar: Solar investments can also increase property value, as discussed earlier. However, the appreciation from solar may not match the value increase from real estate itself. That said, solar can complement real estate investments by providing energy savings, lowering operating costs, and appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
Cost-Effectiveness
Real estate investments typically require larger capital outlays, maintenance costs, and sometimes property taxes. Solar, on the other hand, has relatively low maintenance costs once installed and offers ongoing savings without the need to manage tenants or deal with property-related headaches.
3. Solar vs. Traditional Energy Investments
Many investors may consider putting their money into the traditional energy sector, such as fossil fuels or utilities. How does solar compare?
Fossil Fuels vs. Solar Energy
Investing in traditional energy sources, such as oil and gas, has long been lucrative. However, with growing concerns over climate change and a global shift toward renewable energy, fossil fuels face increasing regulatory and reputational risks. On the other hand, solar energy represents a growing and future-proof market. With government incentives supporting renewable energy, and more companies focusing on clean energy, solar is an attractive long-term investment.

What to Consider Before Investing in Solar Energy
Before diving into solar as a long-term investment, it’s essential to evaluate several factors that could impact the feasibility and profitability of your decision.
1. Assessing Your Home or Business’s Solar Suitability
Not every property is well-suited for solar energy. Factors like roof space, orientation, and local climate can all affect how much energy your solar system can produce. Here’s how to assess if your home or business is a good candidate for solar:
Roof Space and Angle
The size of your roof and its angle are among the most important factors when determining whether solar is a viable option. Solar panels need to be placed on a flat or gently sloped roof with adequate space to capture sunlight efficiently.
- Roof size: Ideally, a south-facing roof that receives plenty of sunlight throughout the day is the best location. The more square footage of your roof that’s available for panels, the more energy you can generate.
- Roof orientation: In the Northern Hemisphere, south-facing roofs typically generate the most solar power because they receive the most direct sunlight. Roofs that face east or west can still work, but they may be less efficient. North-facing roofs typically don’t perform well for solar.
Before investing, it’s a good idea to have a solar assessment performed by a professional installer. They will evaluate your roof’s suitability and determine the ideal system size for your needs.
Energy Consumption
It’s also crucial to assess how much energy your home or business consumes on a regular basis. If you have high electricity bills, a larger solar system may be necessary to meet your needs. On the other hand, if your energy consumption is low, a smaller system may suffice.
- Understanding your energy needs: Review your past electricity bills to estimate how much energy you typically use each month. Solar installers can use this data to help determine the size and capacity of the system required.
- Energy efficiency: If your home or business isn’t energy-efficient, you may need to invest in energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and lighting before installing solar. This will reduce your overall energy consumption, meaning you can install a smaller, less expensive system.
Local Climate
Solar energy production depends on how much sunlight your area receives. If you live in a region with frequent cloud cover, heavy rainfall, or long winters, you may not generate as much energy as you would in sunnier areas. However, it’s worth noting that solar panels can still produce energy on cloudy days — they just won’t generate as much.
- Annual solar exposure: Look into the average amount of sunlight your area receives each year (known as solar insolation). This will give you an idea of how much energy your system can generate over time.
- Shading: Ensure that your roof or property doesn’t have shading from trees, tall buildings, or other obstructions, as this can significantly reduce the amount of solar energy captured.
2. Selecting the Right Solar System and Provider
Once you’ve assessed your property’s suitability for solar energy, the next step is selecting the right solar system and installer. The system you choose will depend on your energy needs, the space available for panels, and your budget. Here’s what you should consider:
Choosing the Right Solar Panels
There are several types of solar panels available, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. The most common types include:
- Monocrystalline Panels: These are the most efficient solar panels, offering high power output in a relatively small space. They’re more expensive but are ideal for properties with limited roof space.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels, but they are more affordable and still provide solid performance for larger systems.
- Thin-Film Panels: These panels are lightweight and flexible, making them ideal for unconventional installations. However, they tend to be less efficient than crystalline options, requiring more space to produce the same amount of energy.
The right type of panel depends on your specific needs, roof size, and budget. If you have limited space, investing in high-efficiency panels may be worth the extra cost.
Choosing a Solar Installer
When selecting a solar provider, it’s important to choose a reputable, experienced company. Look for the following qualities in a solar installer:
- Licensing and Certifications: Ensure the installer is licensed and has proper certifications, such as NABCEP (North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners). This ensures that they are trained and qualified to handle solar installations.
- Experience: Look for companies that have been in the business for several years and have a proven track record of successful installations.
- Customer Reviews and References: Check online reviews, ask for references, and look for customer testimonials to gauge the installer’s reliability and customer service.
- Warranty: Ensure that your installer offers a solid warranty, covering both the equipment and installation. A standard warranty for panels is 25 years, but the workmanship warranty may vary.
Cost and Financing Options
The total cost of installing solar can vary based on system size, location, and installation company. Be sure to get multiple quotes from different providers to compare pricing and available financing options. Many installers offer financing, which can help lower the upfront costs.
- Upfront cost: If you can afford the upfront costs, paying in full can help you save money in the long term (as it avoids interest payments).
- Loans and leases: If upfront costs are a barrier, explore financing options like solar loans, leases, or PPAs.
The Future of Solar as a Long-Term Investment
The solar energy industry is constantly evolving, and several factors are expected to influence the value of solar as a long-term investment in the coming years. Below, we’ll discuss some of the key trends and innovations that could make solar an even better investment in the future.
1. Technological Advancements in Solar Energy
The solar industry is seeing significant advancements in technology that are improving both efficiency and affordability. These innovations could make solar even more appealing as a long-term investment:
- Bifacial Solar Panels: These panels can capture sunlight from both the front and the rear, increasing energy production. This technology is becoming more widespread and could significantly improve the efficiency of solar systems.
- Solar Roofing: Companies like Tesla are developing solar roofing materials that integrate solar cells directly into roofing tiles, offering a sleek and seamless option for homeowners who want to generate energy without traditional panels.
- Advanced Solar Batteries: Energy storage technology continues to improve. More efficient and affordable solar batteries can help homeowners and businesses store excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days, providing greater energy independence.
2. The Role of Solar in the Global Energy Transition
The shift toward renewable energy sources is accelerating. As governments, corporations, and individuals prioritize sustainability, solar energy is expected to play a critical role in the transition to cleaner, greener energy systems.
- Government Support for Renewables: Many governments are introducing green energy policies and subsidies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy. The expansion of the solar investment tax credit and similar incentives may make solar an even more attractive long-term investment.
- Declining Costs of Solar: As technology improves and more solar systems are deployed, the cost of manufacturing solar panels continues to decrease. This trend will likely continue, making solar even more affordable and improving ROI for investors.
3. The Impact of Solar on Energy Independence
As the grid becomes more vulnerable to disruptions—whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or aging infrastructure—solar energy offers a reliable way for homeowners and businesses to maintain energy independence.
In the future, as grid dependence decreases, more people and companies will likely turn to solar energy as a primary power source, further driving demand for solar installations.
Is Solar a Good Long-Term Investment?
So, is solar a good long-term investment? The answer is generally yes—but it depends on your individual circumstances. If you’re in an area with high utility rates, a suitable roof, and a desire to reduce your carbon footprint, solar can be a highly rewarding financial and environmental investment.
- Cost Savings: Solar panels can save you thousands of dollars over time by reducing energy bills.
- Increased Property Value: Solar can increase the value of your home, making it a wise choice for real estate investors.
- Energy Independence: Solar provides greater energy security, insulating you from future energy price hikes and outages.
- Environmental Impact: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that helps reduce your carbon footprint.
However, it’s important to consider the initial costs, financing options, and the suitability of your property before making the investment. If you can afford the upfront costs (or secure financing) and your location and energy needs align with solar’s potential, investing in solar energy is a smart long-term financial decision.
If you’re ready to make the switch to solar, now is a great time to start researching providers and exploring your options. Your future self will thank you for the savings, energy independence, and positive impact on the planet!