As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy, solar power remains one of the most popular and viable sources of green energy. However, solar panels need sunlight to function efficiently, and capturing as much sunlight as possible is essential for optimizing energy output. This is where solar tracking systems come in. These systems adjust the position of solar panels throughout the day to follow the sun’s movement, ensuring that they are always positioned to capture maximum solar energy.
A solar tracking system is a technology that automatically adjusts the orientation of solar panels to follow the sun’s movement. This adjustment ensures that the panels are always facing the sun, maximizing the amount of solar energy they can absorb.
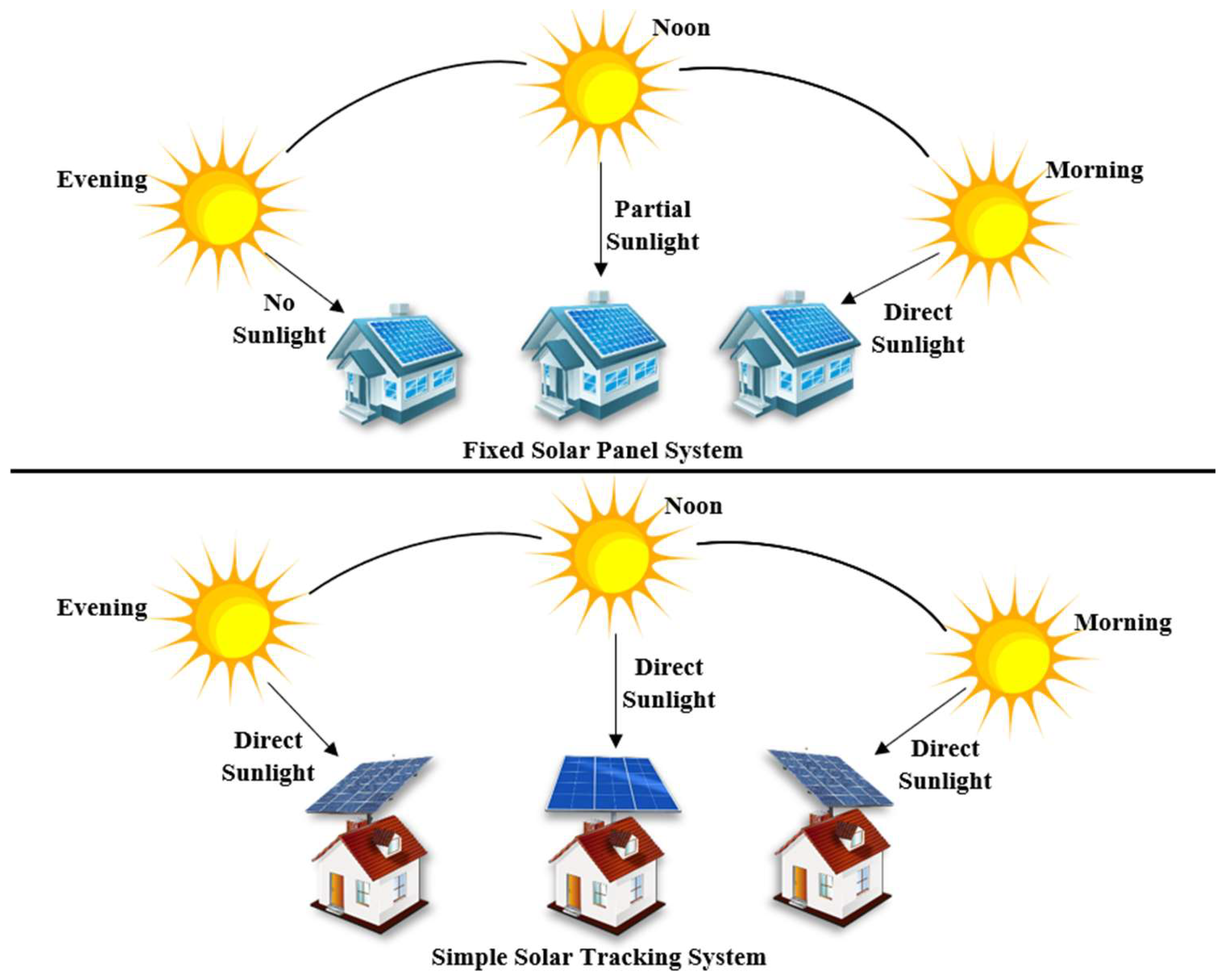
Why is this important? Simply put, the Earth’s rotation causes the sun to move across the sky throughout the day. Fixed solar panels are positioned at a static angle to capture sunlight. While this can be effective, the energy they generate is suboptimal because the panels aren’t always facing the sun as it moves. Solar tracking systems solve this problem by constantly repositioning the panels to follow the sun’s path, ensuring optimal sunlight absorption and, therefore, maximum energy output.
Solar tracking systems are essential for solar farms and large commercial solar installations, where energy efficiency is paramount to ensuring profitability. While these systems are not always necessary for residential use (due to space and budget constraints), they are a popular choice for large-scale operations where efficiency can significantly impact energy production and costs.
How Do Solar Tracking Systems Work?
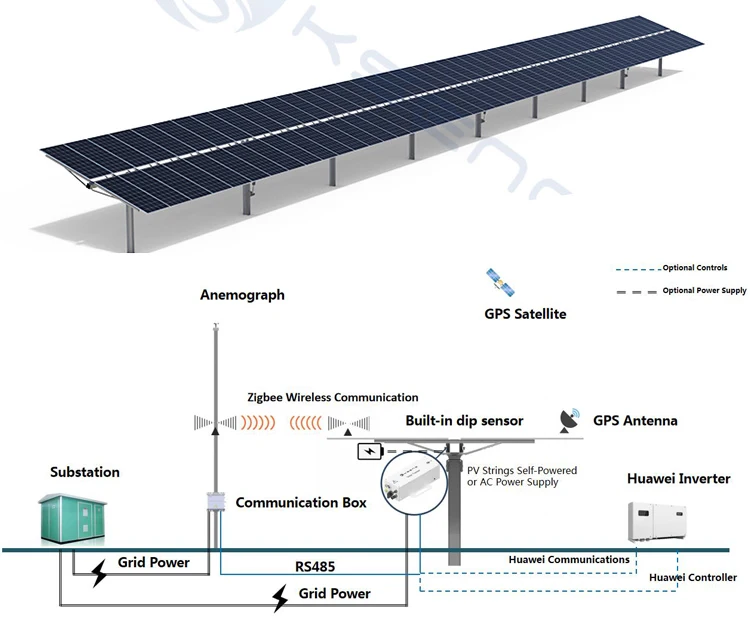
The basic function of a solar tracking system is to adjust the angle of the solar panels so they maintain an optimal position relative to the sun. Solar tracking systems utilize sensors, motors, and control algorithms to detect the sun’s position and adjust the panel’s orientation accordingly.
- Sensors: These detect the sun’s position in the sky. They use either photodiodes (which measure light intensity) or solar sensors (which track the sun’s angle).
- Motors: These are responsible for moving the solar panels to the desired position. The motors adjust the tilt or rotation of the panels.
- Control System: This includes software and hardware that processes the information from the sensors and then directs the motors to adjust the panels accordingly.
Most solar trackers are powered by electric motors and are controlled via a centralized computer system that continuously adjusts the solar panels based on real-time data about the sun’s position.
Solar Tracking System vs Fixed Solar Systems
When comparing solar tracking systems to fixed solar panel systems, several differences arise, particularly in terms of efficiency, cost, and energy output.
| Feature | Fixed Solar Systems | Solar Tracking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Generally less efficient, as panels are fixed at one angle. | 25%–40% more efficient as panels follow the sun’s path. |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront cost. | Higher upfront cost due to complex mechanisms. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs. | Higher maintenance due to moving parts. |
| Energy Production | Lower energy output over time. | Increased energy output, especially in areas with variable sunlight. |
| Space Requirements | Needs less space. | Requires more space due to tracking components. |
Advantages of Fixed Solar Panels:
- Cost-effective: No need for moving parts or complex systems.
- Low maintenance: Fixed systems have fewer mechanical components, reducing the chance of mechanical failure.
Advantages of Solar Tracking Systems:
- Higher energy efficiency: Trackers can increase energy production by up to 40%.
- Better for large-scale operations: For commercial solar farms, the additional energy production justifies the higher cost.
![]()
The Two Types of Solar Tracking Systems
What Are The Two Types of Solar Tracking Systems?
When it comes to solar tracking, there are two primary types: single-axis and dual-axis solar tracking systems. These systems vary in complexity, cost, and efficiency, and each has its unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding these two types of systems is critical in making an informed decision about which one is right for your solar project. Below, we’ll take a deep dive into each of these solar tracking systems, looking at how they work, their benefits, and their most suitable applications.
Single-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
What is a Single-Axis Solar Tracking System?
A single-axis solar tracking system adjusts solar panels along a single axis of rotation, typically moving them from east to west throughout the day. This motion allows the panels to follow the sun’s horizontal path as it rises in the east and sets in the west.
These systems are relatively simple compared to dual-axis trackers because they only track the sun’s daily movement, not its seasonal variations. The panels are usually mounted on a motorized structure that rotates around a horizontal or vertical axis.
- East to West Movement: The motorized frame rotates the solar panels throughout the day to track the sun’s path from sunrise to sunset.
- Tilt Adjustment: In some cases, a small adjustment in the tilt angle is also possible to optimize energy collection, but the primary movement is horizontal.
Pros and Cons of Single-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
Pros:
- Cost-effective: Single-axis trackers are less expensive to install and maintain than dual-axis systems because they involve fewer moving parts.
- Simple Design: With only one axis of rotation, these systems are easier to design and install. They require less complex technology and are more durable.
- Increased Energy Production: Compared to fixed solar systems, single-axis trackers can increase energy output by 20% to 25%, depending on the location and time of year.
- Low Maintenance: Due to fewer moving components, single-axis trackers are easier to maintain than dual-axis systems.
Cons:
- Limited Efficiency Gains: While single-axis systems significantly boost efficiency compared to fixed panels, they still cannot match the energy production gains of dual-axis trackers. They can only track the sun horizontally, which limits their effectiveness compared to dual-axis systems that track both horizontally and vertically.
- Less Effective in Cloudy or Overcast Conditions: In areas with frequent cloud cover, single-axis trackers may not be able to capture sunlight as efficiently, resulting in less effective performance during certain times of the year.
- Space Requirements: These systems require more land area than fixed systems because they must be spaced out to allow the panels to rotate freely without obstruction.
Where Are Single-Axis Solar Trackers Used?
Single-axis solar tracking systems are best suited for large-scale solar farms or commercial applications where maximizing energy production is a priority but budget constraints prevent the use of dual-axis trackers.
- Best for regions with consistent sunlight: Areas where sunlight is available throughout the day, such as deserts or regions with minimal cloud cover, can benefit greatly from single-axis trackers.
- Cost-sensitive projects: For commercial or utility-scale solar farms, single-axis trackers offer a significant energy boost without the higher upfront cost of dual-axis systems.
Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
What is a Dual-Axis Solar Tracking System?
A dual-axis solar tracking system offers more flexibility and precision by adjusting solar panels around two axes—one for horizontal movement (east to west) and one for vertical movement (up and down). This dual-axis movement allows the panels to track the sun’s daily and seasonal motion.
- East to West & Seasonal Adjustment: The panel tracks the sun from sunrise to sunset and adjusts its tilt based on the time of year, optimizing energy capture for both daily and seasonal sun angles.
- Precise Sun Tracking: By adjusting both axes, dual-axis trackers maximize the amount of sunlight the panels receive, which leads to significant efficiency gains.
Pros and Cons of Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
Pros:
- Maximized Energy Production: Dual-axis tracking systems can increase energy output by up to 40% compared to fixed systems, making them ideal for projects where maximizing energy capture is critical.
- Optimal Solar Exposure: These systems can adjust not only for the time of day but also for seasonal changes in the sun’s position. This is particularly valuable in areas closer to the poles where the sun’s angle varies significantly throughout the year.
- Higher Efficiency in Cloudy Regions: Because dual-axis trackers follow the sun more precisely, they tend to be more efficient even on cloudy days, capturing sunlight whenever it’s available.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Dual-axis systems are more expensive to install and maintain due to their complexity. They involve more motors, sensors, and moving parts, which increases both installation and long-term maintenance costs.
- More Maintenance: The added complexity means that dual-axis systems require more maintenance to ensure that all parts are working properly.
- Space Requirements: Dual-axis trackers need more space to allow for the panels to adjust in both horizontal and vertical directions, making them less suitable for smaller installations.
Where Are Dual-Axis Solar Trackers Used?
Dual-axis solar tracking systems are typically found in applications where efficiency and performance are the top priority. They are ideal for:
- High-efficiency solar farms: These trackers are most commonly used in large, commercial-scale solar installations, where the cost of the system is justified by the significant energy production increase.
- Locations with varying sunlight: Regions that experience varying sun angles due to their geographic location benefit from dual-axis trackers, as these systems can adjust for both daily and seasonal changes in the sun’s position.
- Residential applications with sufficient space: For high-end residential applications, dual-axis trackers are sometimes used, particularly when the homeowner seeks the highest level of efficiency and has enough space to accommodate the system.
Differences Between Single-Axis and Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
| Feature | Single-Axis Tracking Systems | Dual-Axis Tracking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 20%-25% more efficient than fixed systems | 30%-40% more efficient than fixed systems |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher initial cost and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance | Requires more maintenance due to complexity |
| Installation Complexity | Easier to install | More complex installation |
| Space Requirement | Needs more land than fixed systems | Requires more space for movement |
| Seasonal Tracking | Tracks daily movement only | Tracks both daily and seasonal movement |
| Best for | Large-scale solar farms and cost-conscious projects | High-efficiency farms or areas with varying sun angles |
Which Tracking System is Right for You?
The choice between single-axis and dual-axis tracking systems depends largely on your budget, energy efficiency needs, and space availability.
- Single-axis systems are best for large-scale installations looking for a cost-effective solution that still boosts energy production by around 20%-25% over fixed panels.
- Dual-axis systems are ideal for those who prioritize maximum energy production and are willing to invest in the higher initial costs and ongoing maintenance.
Both types of systems help solar panel owners extract the most value from their investments by ensuring the panels are always optimally positioned relative to the sun. However, dual-axis trackers provide superior performance in terms of energy yield and are perfect for high-demand or high-efficiency applications.
Differences Between Single-Axis and Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems
Single-Axis vs Dual-Axis Solar Tracking: Key Differences
When choosing between single-axis and dual-axis solar tracking systems, it’s essential to understand how each system differs in terms of efficiency, cost, maintenance, and overall performance. Both types provide substantial improvements over fixed solar panels, but the level of benefit varies based on factors like the location, budget, and the specific goals of your solar installation.
Let’s compare the two systems in a bit more detail:
| Feature | Single-Axis Solar Tracking Systems | Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 20%-25% more efficient than fixed panels. | 30%-40% more efficient than fixed panels. |
| Cost of Installation | More affordable, typically lower upfront costs. | Higher initial cost due to complexity and extra components. |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs; fewer moving parts. | Higher maintenance needs due to additional motors and sensors. |
| Space Requirements | Requires more space than fixed panels due to rotation. | Requires more space, but for different reasons (vertical and horizontal movement). |
| Suitability for Varying Sunlight | Works well in areas with consistent sunlight. | Ideal for regions with varying sunlight, including areas with significant seasonal changes. |
| Best Use Case | Large commercial or utility-scale solar farms where cost efficiency is prioritized. | High-efficiency applications where maximizing energy yield is a top priority. |
| Technological Complexity | Simpler technology with one axis of rotation. | More complex, with two axes of rotation for precise solar tracking. |
Which Solar Tracking System is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between single-axis and dual-axis solar tracking systems ultimately depends on your specific needs, budget, and installation goals. Here’s a breakdown of factors to consider:
- Energy Efficiency Needs:
- If you are looking for the maximum energy yield and are willing to invest more upfront, a dual-axis tracking system is the best choice. It provides the highest increase in energy production by allowing your panels to follow the sun’s movement both throughout the day and across seasons.
- However, if energy efficiency is important but you have a limited budget, a single-axis system will still provide a significant improvement over fixed solar panels.
- Budget:
- Single-axis systems are more budget-friendly, with a lower initial investment and easier installation. If you’re working within a tight budget, this is a cost-effective way to improve solar panel performance.
- Dual-axis systems have a higher upfront cost and maintenance requirements, so they are more suitable for projects where long-term energy savings outweigh the initial costs. They are ideal for commercial and large-scale solar farms.
- Location and Climate:
- If your installation is in a sunny, consistent climate where sunlight is available throughout the day, a single-axis tracker will provide enough efficiency boost.
- For areas with seasonal changes or locations closer to the poles where the sun’s position changes dramatically throughout the year, a dual-axis tracker is highly beneficial. These systems are better suited for regions with varying sun angles due to their ability to adjust for both daily and seasonal sun paths.
- Space Availability:
- Dual-axis systems require more space because they need extra room for both horizontal and vertical movement. They are typically better for installations where land is available in abundance (e.g., large commercial projects).
- Single-axis systems, though they require more space than fixed systems, need less space than dual-axis trackers. They are a good middle ground for projects with space constraints but still want the benefit of solar tracking.
- Maintenance Considerations:
- Single-axis trackers are generally easier and cheaper to maintain because they have fewer moving parts and simpler designs.
- On the other hand, dual-axis systems require more maintenance and monitoring due to their complexity. They involve more components (such as motors, sensors, and control systems), all of which need periodic checks to ensure optimal functionality.
Which System is Best for Your Project?
If you’re working on a large-scale solar farm or a high-efficiency solar project, and budget is not a constraint, then a dual-axis tracking system is the clear winner. Its ability to adjust to both daily and seasonal variations in the sun’s position will give you the highest energy production and make the most efficient use of the available sunlight.
However, if you’re working on a commercial project or are looking to enhance the performance of existing solar panels without breaking the bank, a single-axis solar tracker offers a great balance of cost-efficiency and energy production. It delivers significant improvements over fixed systems at a fraction of the price of dual-axis trackers, making it an attractive option for those seeking more efficiency at a lower cost.
Benefits of Solar Tracking Systems
Why Use a Solar Tracking System?
When considering the installation of a solar tracking system, the primary reason for doing so is to maximize energy production. Solar tracking systems are designed to keep solar panels aligned with the sun, ensuring they capture as much sunlight as possible. But beyond this obvious benefit, solar trackers offer several key advantages that can significantly enhance the performance and profitability of solar energy systems.
Here are some of the top benefits of using solar tracking systems:
1. Increased Energy Production
The most significant benefit of solar tracking systems is their ability to increase energy production. By adjusting the orientation of solar panels to follow the sun’s path across the sky, tracking systems ensure that panels are always positioned at the optimal angle for sunlight absorption.
- Single-axis trackers can increase energy output by up to 25% compared to fixed systems.
- Dual-axis trackers offer even greater improvements, with energy production increases of up to 40% compared to fixed panels. This can be especially valuable in high-demand energy applications or when solar panels are used to supply power to multiple homes or businesses.
In essence, tracking systems make solar panels much more productive by ensuring they absorb as much solar energy as possible throughout the day and year.
2. Reduced Land Use for Large-Scale Solar Projects
Solar farms require a significant amount of land to generate enough power to meet energy needs. While fixed solar panels need to be spaced out to avoid shading, solar tracking systems can reduce the amount of land required for large-scale solar projects.
- Single-axis trackers allow for panels to be spaced more closely together, as they only need enough room to rotate from east to west.
- Dual-axis trackers, while needing more space for movement, can also optimize energy output in smaller land areas by maximizing the sunlight captured from both horizontal and vertical movements.
For developers looking to maximize energy output without expanding the land area, solar tracking systems offer a clear solution. By increasing efficiency, trackers allow solar farms to generate more electricity per square foot, which can ultimately reduce costs.
3. Environmental Benefits: Maximizing Clean Energy
Solar power is one of the cleanest energy sources, contributing to a significant reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power sources. By using solar tracking systems, solar installations can maximize the amount of renewable energy they produce, which helps offset more fossil fuel consumption.
- Maximized solar energy capture means more green energy produced.
- For large-scale solar farms, maximizing output per square foot can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of energy production, helping combat climate change and pollution.
Whether you’re working on a residential solar system or managing a large solar farm, solar tracking systems contribute to a more sustainable energy future by ensuring that solar energy is being used efficiently.
4. Improved Return on Investment (ROI)
Although solar tracking systems come with a higher upfront cost compared to fixed panels, they tend to deliver better long-term financial returns. Here’s why:
- Increased Energy Production: As discussed, trackers can boost energy production by up to 40%. This means you will generate more power per unit of energy, leading to greater savings on electricity bills or higher revenue if selling energy back to the grid.
- Higher Efficiency: More energy production leads to a faster return on investment (ROI). For businesses and commercial users, the increased output from solar trackers can result in quicker payback periods, making the additional initial investment worthwhile in the long term.
For those considering solar installations for commercial or utility-scale purposes, solar trackers provide a compelling reason to invest in the extra technology and maintenance, thanks to their higher yields.
5. Adaptability in Different Climates
Another benefit of solar tracking systems, especially dual-axis trackers, is their ability to perform well in a variety of climates. Since they adjust for both the time of day and seasonal variations, they’re particularly suited for regions where the sun’s angle changes drastically depending on the time of year.
- Dual-axis systems are ideal for areas with extreme seasonal variations in sun angles, such as regions closer to the poles, or those with long winters or frequent cloud cover.
- Single-axis systems, while less efficient in regions with high seasonal variation, are still beneficial in more temperate climates where sunlight is fairly consistent.
Overall, solar trackers can be adapted to different geographic regions, making them a versatile solution for maximizing solar efficiency no matter where you live.
How Much More Energy Can a Solar Tracking System Generate?
One of the main questions about solar tracking systems is how much additional energy they can produce compared to fixed solar panels. On average:
- Single-axis tracking systems increase energy output by approximately 20%-25% over fixed systems, mainly due to their ability to track the sun’s movement throughout the day.
- Dual-axis tracking systems provide even greater efficiency, increasing energy output by 30%-40%. These trackers are especially beneficial in regions with seasonal sunlight changes or where maximum energy capture is necessary.
In practice, this means that solar installations with tracking systems can generate far more energy over the course of a year, providing a stronger return on investment and increasing the overall efficiency of solar power systems.
Can Solar Tracking Systems Save You Money in the Long Run?
The question of long-term savings is a key consideration when choosing between fixed solar panels and solar tracking systems. While the upfront costs for trackers are higher, their ability to increase energy output typically leads to greater cost savings over time.
- With increased energy production from tracking systems, you can reduce reliance on grid power, lowering electricity bills. In commercial settings, the increased output can help offset operational costs.
- Higher energy yield means that you will reach payback faster, shortening the time needed to recoup the initial investment. For some commercial or large-scale projects, this can mean achieving positive cash flow much sooner than with fixed systems.
For businesses and large solar farms, the return on investment for solar tracking systems is clear, even though the initial investment is higher. For residential users, the added energy production can also contribute to a quicker return, especially if the area experiences high amounts of sunlight year-round.